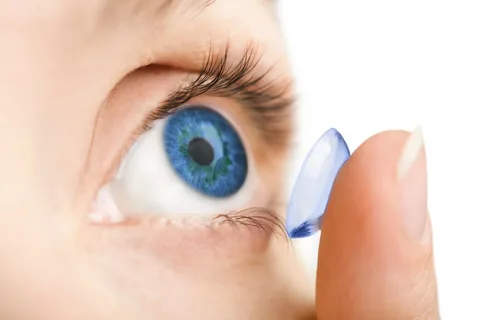
Contacts lenses are a popular volition to spectacles, offering freedom from frames while still correcting vision. Whether you need them for hypermetropia, vision, presbyopia, or indeed ornamental purposes, contacts lenses have revolutionized the way we manage vision correction. In this comprehensive companion, we will explore the different types of contact lenses, how to duly watch for them, their benefits, and implicit pitfalls.
1. What Are Contact Lenses?
Contacts lenses are thin, twisted lenses that sit directly on the face of the eye. They correct refractive crimes by fastening light duly onto the retina, perfecting vision. Unlike spectacles, connections move with the eye, furnishing a natural field of vision without inhibition or deformation.
Connections are made from a variety of accoutrements , depending on the type and purpose. utmost ultramodern lenses are made of soft, flexible plastics like silicone hydrogel, which allow oxygen to pass through, keeping the eyes healthy.
2. Types of Contact Lenses
contacts lenses come in numerous different types to suit different requirements and preferences. Then are the most common bones
a) Soft Contact Lenses
Soft lenses are the most popular type, favored for their comfort and breathability. They’re made of soft, flexible accoutrements that conform to the shape of the eye. Soft lenses come in colorful orders
diurnal wear and tear lenses These lenses must be removed before sleeping and generally replaced daily, daily, or monthly, depending on the brand.
Extended wear and tear lenses These can be worn for over to 30 days continuously, including overnight, though they bear regular cleaning to avoid infections.
Disposable lenses These are meant for single use and are discarded after one day. They’re ideal for people with disinclinations or who are prone to eye infections, as they do not bear cleaning.
b) Rigid Gas Passable( RGP) Lenses
RGP lenses, also known as hard lenses, offer clearer vision than soft lenses in certain cases, particularly for people with presbyopia or more complex conventions. They’re more durable and generally last longer, but they bear a longer adaptation period and are less comfortable originally than soft lenses.
c) Toric Lenses
Toric lenses are designed for people with presbyopia, a condition where the cornea is desultorily shaped, causing blurred vision. These lenses have different powers in different meridians of the lens to correct the irregular curve of the eye.
d) Multifocal/ Bifocal Lenses
For those with diplopia, an age- related condition where the eye loses the capability to concentrate on close objects, multifocal or bifocal lenses offer a result. These lenses give both near and far vision correction in a single lens.
e) Cosmetic Lenses
Colored or ornamental contacts lenses are used to change the appearance of the eyes. While numerous people wear them purely for aesthetic reasons, tradition performances are available to combine vision correction with eye color change. It’s important to note that ornamental lenses bear the same care and medical supervision as regular lenses.
3. Benefits of Contact Lenses
Contact lenses offer several advantages over traditional spectacles
a) bettered Field of Vision
Since contacts lenses rest directly on the eye, they give a full field of vision without any frames gumming supplemental sight. This makes them especially useful for sports or other conditioning that bear a wide field of view.
b) Aesthetic Benefits
numerous people prefer contacts lenses because they allow for a more natural look without the presence of spectacles. For some, spectacles may not suit their particular style, while others may not like the way spectacles feel on their face.
c) Convenience
contacts lenses do n’t fog up in cold rainfall, do n’t get wet in the rain, and do n’t slip down your nose like spectacles do. They’re ideal for active cultures, especially during sports, where spectacles can be clumsy or dangerous.
d) Eye Conditions
For certain eye conditions like keratoconus( where the cornea becomes cone- shaped) or severe presbyopia, contacts lenses give better vision correction than spectacles by putrefying to the shape of the eye more directly.
4. How to duly watch for Your Contact Lenses
Proper care and hygiene are pivotal for maintaining healthy eyes and avoiding infections. Then’s how to take care of your lenses
a) Wash Your Hands
Always wash your hands with cleaner and water before touching your contacts lenses. Avoid using poultices or unctuous detergents, as they can leave a residue on your lenses.
b) Use the Correct Cleaning Solution
Never use valve water or slaver to clean your lenses. Always use the contacts lens result recommended by your eye croaker , as it’s designed to disinfect and hydrate the lenses.
c) Clean and Store duly
still, clean them daily with the applicable result, If you are using applicable lenses. Store them in a clean lens case filled with fresh result. Replace the case every three months to help bacteria buildup.
d) Follow the relief Schedule
Indeed if your lenses feel fine, it’s important to stick to the relief schedule specified by your eye croaker . Wearing lenses past their relief date increases the threat of eye infections.
5. Implicit pitfalls and Complications
While contacts lenses are generally safe, indecorous use or care can lead to complications. Some of the pitfalls include
a) Eye Infections
One of the most common pitfalls of wearing contacts lenses is eye infection. This can be when lenses are n’t gutted duly or worn for too long. The most serious infection, microbial keratitis, can lead to blindness if not treated instantly.
b) Dry Eye
Wearing contacts lenses can occasionally beget or worsen dry eye symptoms. This happens because lenses can reduce the quantum of oxygen reaching the cornea and can affect tear product. Using rewetting drops or switching to lenses designed for dry eyes can help palliate this issue.
c) Corneal Ulcers
Corneal ulcers are open blisters on the cornea, generally caused by bacterial infections from indecorous lens hygiene. They can be painful and, in severe cases, lead to endless vision loss.
d) Antipathetic responses
Some people may develop antipathetic responses to the contacts lens material or the cleaning result, leading to discomfort, greenishness, or vexation.
6. Consulting with an Eye Care Professional
Before switching to or starting with contacts lenses, it’s pivotal to consult an eye care professional. They will perform a comprehensive eye test to insure your eyes are healthy enough for contact lenses. They’ll also help you choose the right type of lenses grounded on your life, tradition, and any beginning conditions like dry eye or presbyopia.
also, regular check- ups are essential to cover the health of your eyes and insure the lenses are befitting rightly. Your eye croaker will also give tips on maintaining lens hygiene and what to do in case of discomfort or an infection.
7. Conclusion
contacts lenses offer a protean and accessible way to correct vision, but they come with liabilities. Proper care, hygiene, and regular consultations with an eye care professional are vital to insure that your eyes remain healthy and comfortable. With the right type of lenses and care routine, contact lenses can give clear vision and freedom from spectacles for times to come.